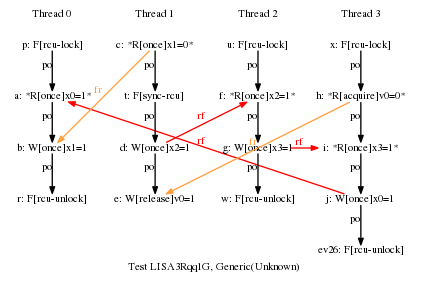
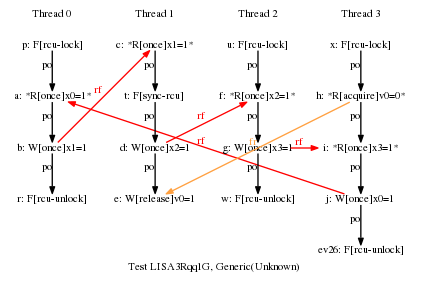
LISA LISA3Rqq1G
(*
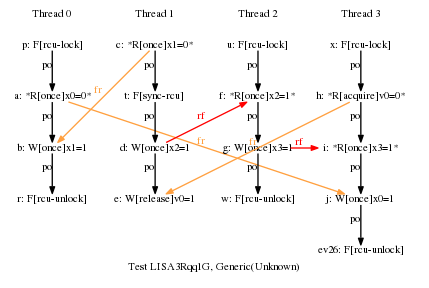
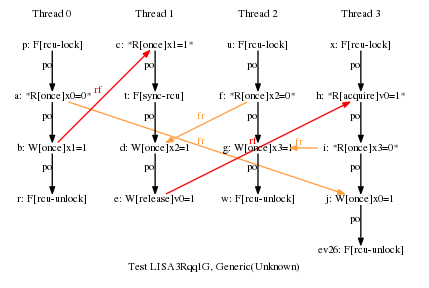
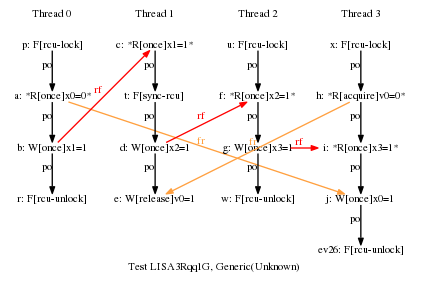
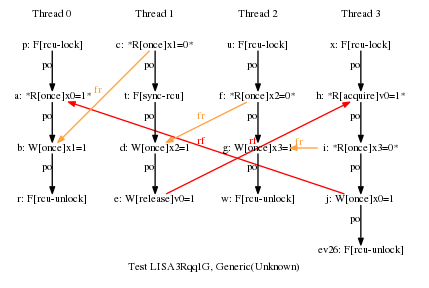
* Result: Never
*
* One RCU grace period and three RCU read-side critical sections.
* This would normally allow the cycle, but there is a release-acquire
* relationship between P1 and P3, which forces all of P3 to follow
* the grace period. One key point of this example is that this
* added release-acquire pair prevents the misordering that would
* normally be provided by P2's RCU read-side critical section,
* despite the fact that there has been absolutely no change to P2.
* So good luck working this stuff out via local reasoning!!! ;-)
* Cycle prohibited.
*)
{
x0 = 0;
x1 = 0;
x2 = 0;
x3 = 0;
v0 = 0;
}
P0 | P1 | P2 | P3 ;
f[rcu_read_lock] | r[once] r1 x1 | f[rcu_read_lock] | f[rcu_read_lock] ;
r[once] r2 x0 | f[sync] | r[once] r2 x2 | r[acquire] r4 v0 ;
w[once] x1 1 | w[once] x2 1 | w[once] x3 1 | r[once] r3 x3 ;
f[rcu_read_unlock] | w[release] v0 1 | f[rcu_read_unlock] | w[once] x0 1 ;
| | | f[rcu_read_unlock] ;
Observed
3:r4=0; 3:r3=1; 2:r2=1; 1:r1=1; 0:r2=1;
and 3:r4=0; 3:r3=1; 2:r2=1; 1:r1=0; 0:r2=1;
and 3:r4=1; 3:r3=0; 2:r2=0; 1:r1=0; 0:r2=1;
and 3:r4=0; 3:r3=1; 2:r2=1; 1:r1=1; 0:r2=0;
and 3:r4=1; 3:r3=0; 2:r2=0; 1:r1=1; 0:r2=0;
and 3:r4=0; 3:r3=1; 2:r2=1; 1:r1=0; 0:r2=0;





